Acquisition systems
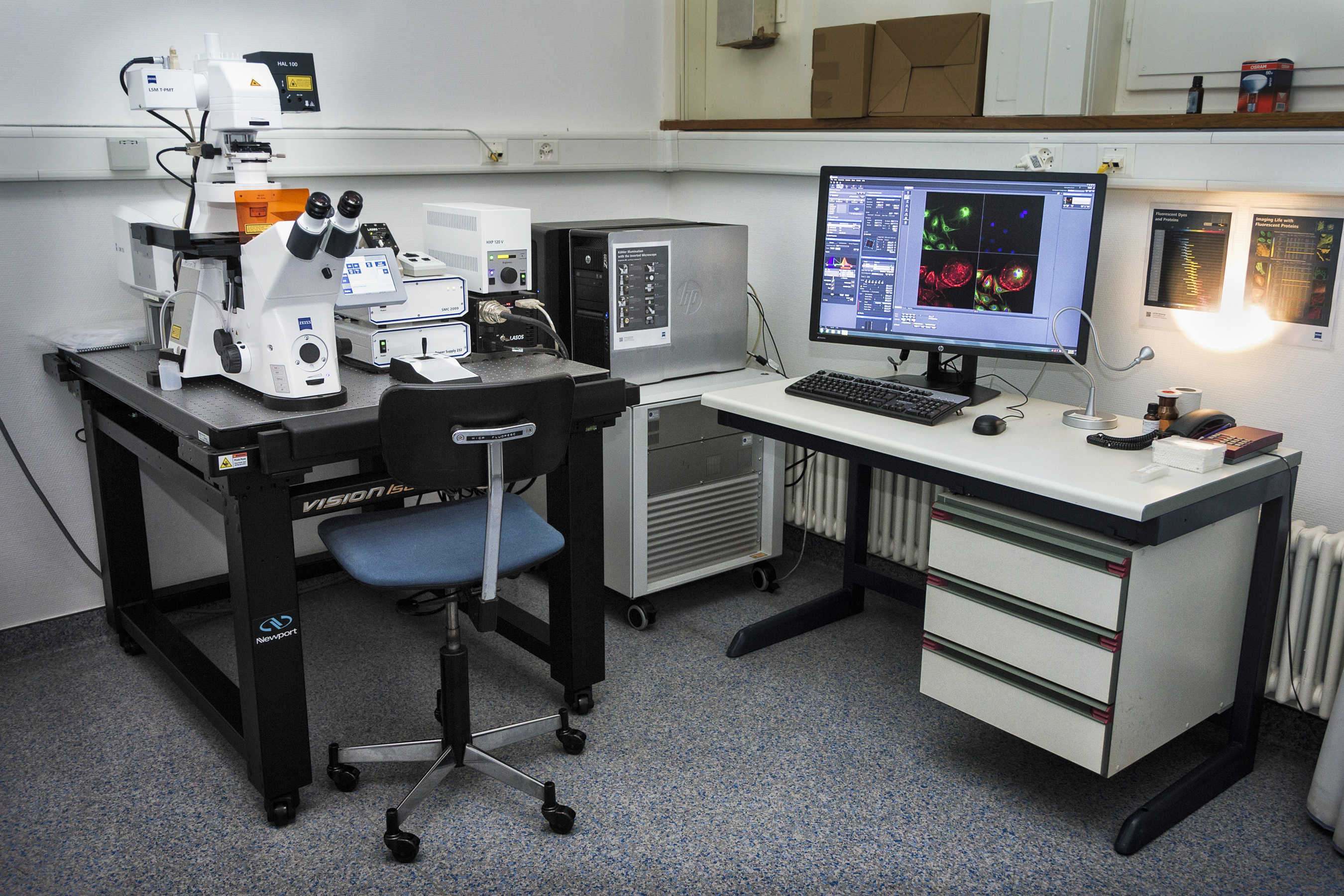
Confocal
Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser confocal scanning microscopy (LCSM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out-of-focus light in image formation.[1] Capturing multiple two-dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures (a process known as optical sectioning) within an object.
Leica Stellaris 8
| Stand |
|
|
Illumination |
|
|
Lasers |
|
|
Objectives |
|
|
Stage |
|
|
Contrast |
|
|
CO2 | T° control |
|
|
Incubation type |
|
|
Detector type |
|
|
Camera |
|
|
Optional modules |
|
|
Software |
|
|
Room |
|
Zeiss LSM 780 with Airyscan
| Stand |
|
| Widefield Illumination |
|
| Lasers |
|
| Objectives |
|
| Stage |
|
| Contrast |
|
| CO2 | T° control |
|
| Detector type |
|
| Optional modules |
|
| Software |
|
| Location |
|
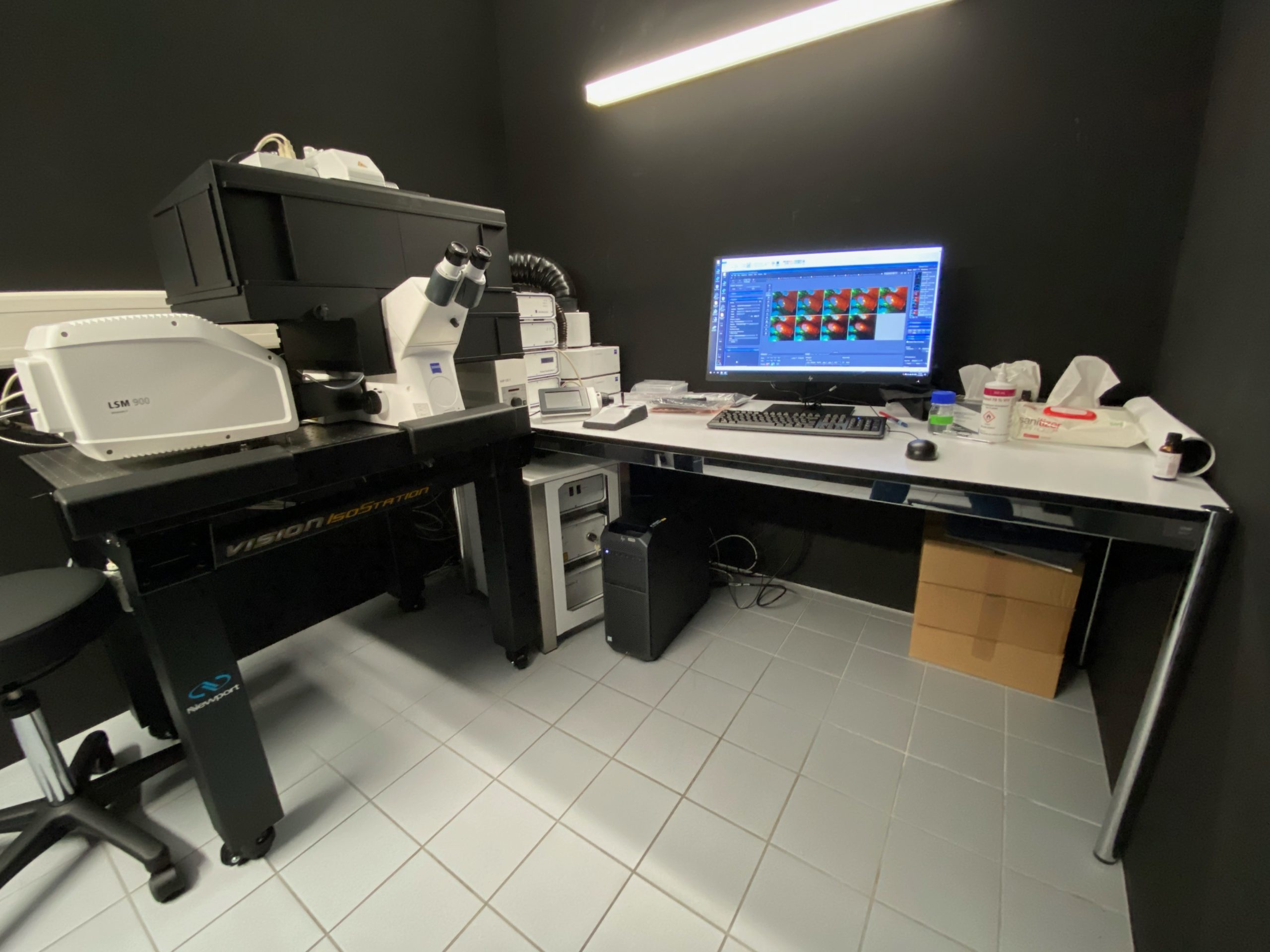
Zeiss LSM 900
| Stand |
|
| Widefield Illumination |
|
| Lasers |
|
| Objectives |
|
| Stage |
|
| Contrast |
|
| Cubes |
|
| CO2 | T° control |
|
| Detector type |
|
| Optional modules |
|
| Software |
|
| Location |
|
Zeiss LSM 900 BSL-2 Lab [SPECIAL AUTHORIZATION REQUIRED]
This particular setup being placed in a BSL-2 (Bio Safety Level 2) Lab, a special authorization is required to access it.
The management and access to this BSL-2 confocal microscope is under the direct supervision of IMUL (contact: Jérôme Gouttenoire, Jerome.Gouttenoire@chuv.ch, + 41 79 556 60 93 – or- Nicolas Jacquier, Nicolas.Jacquier@chuv.ch, +41 21 314 8539
| Stage |
|
|
Illumination |
|
|
Lasers |
|
|
Objectives |
|
|
Stage |
|
|
Contrast |
|
|
CO2 | T° control |
|
|
Detector type |
|
|
Optional modules |
|
|
Software |
|
|
Room |
|
Spinning Disk | Time-Lapse
Spinning-disk (Nipkow disk) confocal microscopes use a series of moving pinholes on a disc to scan spots of light. Since a series of pinholes scans an area in parallel, each pinhole is allowed to hover over a specific area for a longer amount of time thereby reducing the excitation energy needed to illuminate a sample when compared to laser scanning microscopes. Decreased excitation energy reduces phototoxicity and photobleaching of a sample often making it the preferred system for imaging live cells or organisms.
Nikon Ti2 | CrEST Optics X-Light V3
| Stand |
|
|
Spinning Disk Head |
|
|
Widefield LED Illumination |
Lumencor Sola LED |
|
Filter Cubes |
|
|
Spinning Disk + DMD LED excitation |
Spinning Disk: Lumencor Celesta
DMD: Lumecor Spectra X
|
|
Objectives |
|
|
Stage |
|
|
Contrast |
|
|
CO2 | T° control |
|
|
Cameras |
|
|
DMD |
|
|
Optional modules |
|
|
Software |
|
|
Room |
|
Widefield | Fluorescence
The majority of fluorescence microscopes, especially those used in the life sciences, are of the epifluorescence design shown in the diagram. Light of the excitation wavelength illuminates the specimen through the objective lens. The fluorescence emitted by the specimen is focused to the detector by the same objective that is used for the excitation which for greater resolution will need objective lens with higher numerical aperture. Since most of the excitation light is transmitted through the specimen, only reflected excitatory light reaches the objective together with the emitted light and the epifluorescence method therefore gives a high signal-to-noise ratio. The dichroic beamsplitter acts as a wavelength specific filter, transmitting fluoresced light through to the eyepiece or detector, but reflecting any remaining excitation light back towards the source.
Leica DMi8
| Stand |
|
|
Illumination |
|
|
Filters |
|
|
Objectives |
|
|
Stage |
|
|
Contrast |
|
|
CO2 | T° control |
|
|
Cameras |
Color camera
Black and White Camera
|
|
Optional modules |
|
|
Software |
|
|
Room |
|
Stereomicroscopy
The stereo, stereoscopic or dissecting microscope is an optical microscope variant designed for low magnification observation of a sample, typically using light reflected from the surface of an object rather than transmitted through it. The instrument uses two separate optical paths with two objectives and eyepieces to provide slightly different viewing angles to the left and right eyes. This arrangement produces a three-dimensional visualization of the sample being examined.[1] Stereomicroscopy overlaps macrophotography for recording and examining solid samples with complex surface topography, where a three-dimensional view is needed for analyzing the detail.
Nikon SMZ25 Stereomicroscope | Macroscope
| Stand |
|
|
Illumination |
|
|
Filters |
|
|
Objectives |
|
|
Stage |
|
|
Contrast |
|
|
CO2 | T° control |
|
|
Cameras |
|
|
Optional modules |
|
|
Software |
|
|
Room |
|
Slide scanner
A slide scanner allows you to digitize full microscopy slides in an automated manner. This is a high througput system able to process around a hundred of slides in one batch.
Zeiss Axioscan Z.1
The way the Zeiss slide scanner works at the CIF implies that designing a specific profile for each of your sample type is needed.
This profile is very dependent of the way you have prepared your slides. Since this processe is time-consuming, it is only useful if you have at least a dozen or more slides of the exact same type to acquire (1-2 hours with testing).
Here are some general guidelines before thinking of using the slide scanner for your experiments:
|
SCAN PROFILE |
|---|
|
If the samples vary in any one of these categories:
Fluorescence specific:
The profile will have to be updated and saved as a new variant or it will probably fail (not focused, over/underexposed, stitching failing). |
|
ACQUISITION TIME |
|
The acquisition time depends on:
Each of these parameters can greatly vary the acquisition time, which can range from a few minutes to an hour or more per slide. |
|
DATA SETS |
|
The files are acquired in the .CZI format.
|
|
Illumination |
Zeiss Colibri 7 Type R[G/Y]CBV-UV
|
|
Filters |
|
|
Objectives |
|
|
Stage |
|
|
Contrast |
|
|
CO2 | T° control |
|
|
Cameras |
Color camera
Black and White Camera
|
|
Optional modules |
|
|
Software |
|
|
Room |
|
Image Processing
[Under construction]